Web Design Essentials 1
Class 4
AGENDA
- Class 3 Review
- Basic CSS Properties (contd)
- CSS Box Model
- Block vs Inline Elements
- Box-Sizing Property
- "CSS Reset"
- Class 5 Preview
- Class Feedback and Q&A
Stretch - "Bio" Break
8:00p EST / 7:00p CST / 5:00p PST
CSS Properties (contd)
CSS Color Values
Browsers can accept colors in different ways:
| Color name: | red |
| Hexadecimal value: | #FF0000 |
| RGB value: | rgb(255, 0, 0) |
| RGBa value: | rgb(255, 0, 0, 1) |
| HSL value | hsl(0, 100%, 50%) |
Color Values Demo
Common Size Units
- Pixels: px
- Root element font-size: rem
- Default root font-size: 16px
- Element font-size: em
- Percentage: %
Size Units Demo
Fonts
Web Safe Fonts
- Fonts that all browsers can display by default
- They don't have to be loaded into our projects
- They don't have to be linked from an external source
- Web safe fonts can be used as "fallbacks" for custom fonts
p {
font-family: "Times New Roman"; /* Specific font name */
font-family: serif; /* Generic name */
font-family: "Arial", sans-serif; /* Comma-separated list */
}
Custom Fonts
Two ways to apply custom fonts:
- Load font files into our project directory, or
- Link to external font libraries such as Google Fonts
Google Fonts
Demo
CSS Box Model
Boxes Everywhere!
Every HTML element on a page is wrapped in a box.
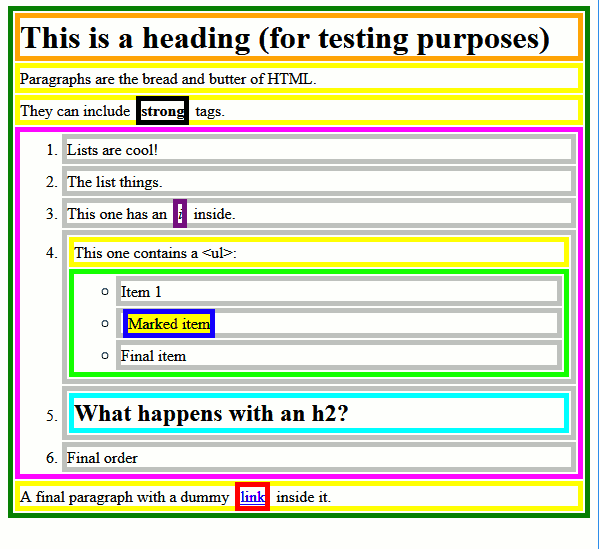
Image source: complete-concrete-concise.com
Box Model Properties
- Content: Text, image, form, etc.
- Padding:The space around the content, or the distance between the content and its borders
- Border:The wrapper around the content and its padding
- Margin: The distance between an element and its neighbors
Box Model
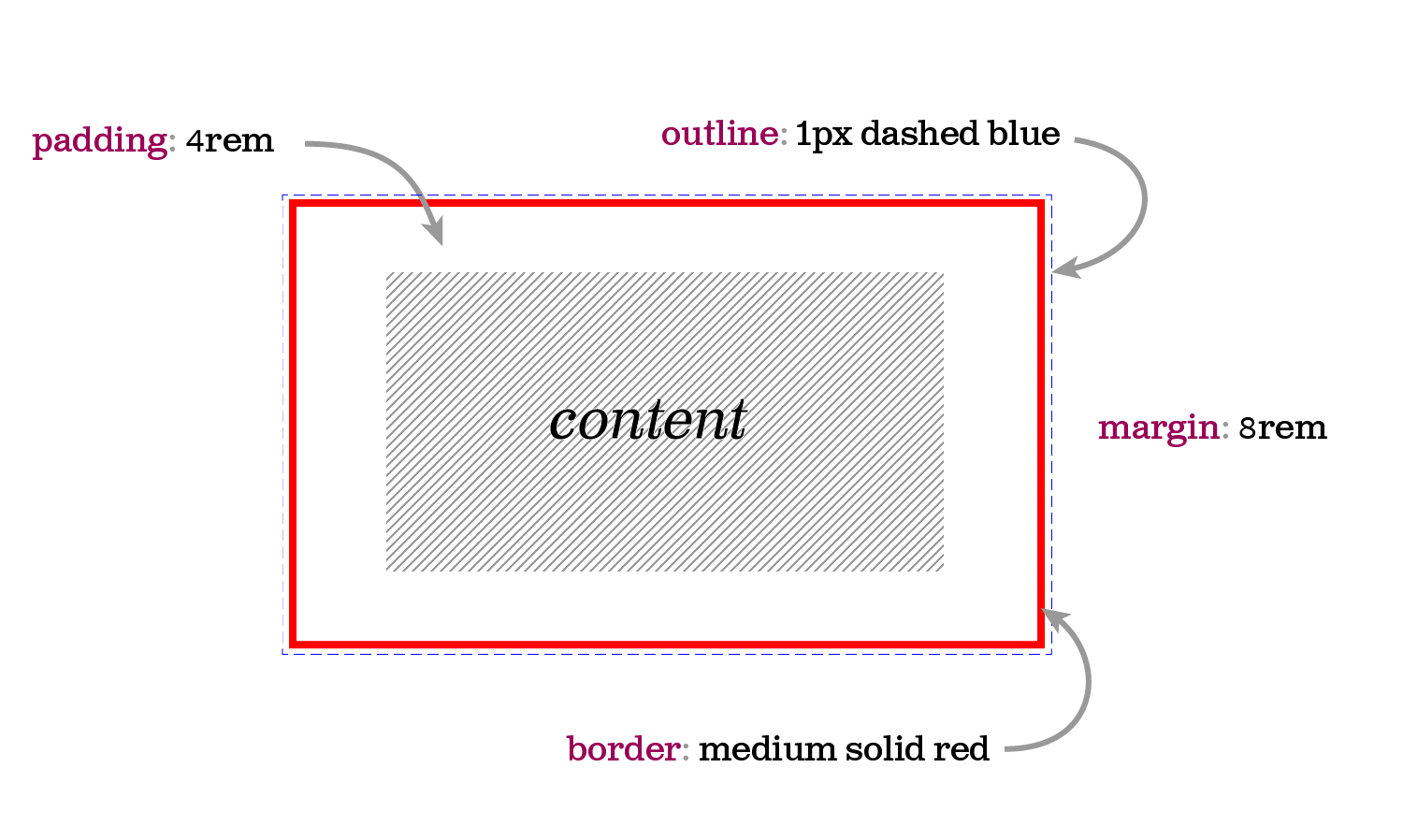
Image source: thenewcode.com
Box Model in Developer Tools
Demo
Display Flow
Every element has a default flow or way that it renders on the page before any CSS styling is applied. It is either:
- Stacking on top of another element
- Side by side with another element
Block and Inline Elements
- Elements that stack are:
Blockelements - Elements that are side-by-side on the same line are
Inlineelements
This is also referred to as an element's display property.
Block vs Inline Behavior
- Block elements start a new line or live on their own line; they take up the full width of their line or their parent container
- Inline elements don't start a new line and take up only as much space as their content needs
Block Elements
Block-level elements include:
- Headings (h1, h2, etc)
- Paragraphs
- Divs
- Lists
Inline Elements
Inline-level elements include:
- Anchor "a" tags
- Images
- Spans
The CSS "Display" Property
- CSS can be used to change an element's default flow or display property
- A block element can be changed to an inline element and vice versa
The CSS "Display" Property
/* This paragraph element will now be an inline element */
p {
display: inline;
}
/* This span element will now be a block element */
span {
display: block;
}
Block and Inline Elements
Demo
Layout Pitfalls
A few default properties of CSS can lead to unexpected layout behavior. There are two common culprits:
- the CSS property
box-sizing - Browser defaults
Box-Sizing
The CSS box-sizing property determines how we calculate the total width and height of an element. It has two values:
/* content-box is the default box-sizing
value of all elements */
box-sizing: content-box;
/* border-box will be your layout's best friend! */
box-sizing: border-box;
Layout Tip #1
Set the box-sizing property of all elements in your project to border-box.
/* This declaration will target every element in the project */
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
Box Sizing
Demo
Layout Tip #2
Use CSS resets.
Browser Defaults
- Most HTML elements have one or more default browser values, that is, they have some basic CSS that influences their appearance on a page
- Some of these defaults can throw off our page layout; others may not be needed
Resetting CSS
- A "CSS Reset" stylesheet is one way to remove some of these defaults globally in our project
- In this stylesheet, we are writing new CSS values to overwrite the browser defaults
CSS Resets
You can create your own reset rules or use any number of well-known reset stylesheets such as:
Two Ways to Reset
- Add a separate reset.css stylesheet to your project with the
linktag in theheadsection of your HTML page- Make sure the link comes before the project's stylesheet link
- Include/Import the new CSS rules at the top of your project's stylesheet
CSS Reset
Demo
Home Practice
- Continue refining your page markup
- Continue styling with CSS properties we've covered and/or other properties you look up!
- Add custom font(s) from Google Fonts
- Optional: Share your layout sketch and markup with me:
- Image link to your sketch
- Your REPL project link
Class 5 - Agenda
- CSS Box Model (contd)
- CSS Combinators & Pseudo-Classes
- Working with Images
- Responsive Web Design
- Media Queries
Q&A
Class Feedback
